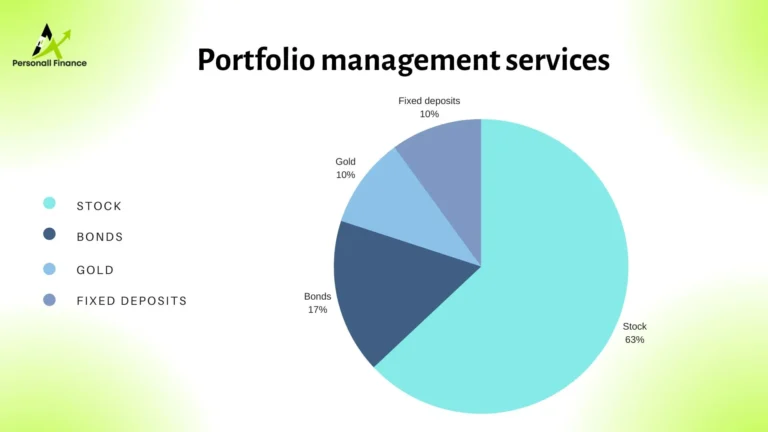
Introduction
In the complex the world of finance and stock market investments, one term that holds significant influence is “ROE” or Return on Equity. But what exactly does ROE signify, and why should it matter to both experienced investors and those just stepping into the world of stocks? In this easily understandable guide, we’ll delve into the meaning of ROE, how it’s computed, its advantages, its limitations, and the important role it plays in the world of stock investing
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is ROE.
ROE, or Return on Equity, is a financial metric that acts as an indicator for how effectively a company uses the funds provided by its shareholders to generate profits. Think of it as evaluating a chef’s skill in using ingredients to cook up a delicious dish. In the stock market arena, ROE acts as a beacon, illuminating how efficiently a company utilizes shareholders’ investments to boost its earnings.
ROE Formula
The computation of ROE is surprisingly straightforward. It involves dividing a company’s net income by its shareholders’ equity and expressing the result as a percentage. Here’s the formula in action:
[ ROE = \frac{Net Income}{Shareholders’ Equity} \times 100 \]
For instance, if a company has raked in a net income of ⟨₹500,000, and its shareholders’ equity stands at ₹2,000,000, the calculation would look like this:
[ ROE = \frac{500,000}{2,000,000} \times 100 = 25% \]
In this illustrative scenario, the company’s ROE stands at a respectable 25%.
Advantages of ROE
1. Performance Evaluation: ROE provides investors with a potent tool to evaluate a company’s performance. A higher ROE generally signifies efficient management of shareholders’ investments.
2. Comparative Analysis: Investors may use ROE for comparisons that are comparable across companies in the same industry, facilitating informed investment choices.
3. Profitability Insight: It’s a fundamental gauge of a company’s profitability and its knack for generating earnings from shareholder resources.
Limitations of ROE
1. Industry-Specific Variations: ROE can vary significantly across industries, rendering a one-size-fits-all approach unsuitable. What constitutes a good ROE in one sector might not hold true for another.
2. Influence of Debt: Companies can artificially inflate their ROE by taking on substantial debt, which can entail risks and prove unsustainable.
3. Short-Term Bias: Dependent just on ROE may foster a short-term perspective, which may not be beneficial to long-term investments.
Conclusion
Return on Equity (ROE) serves as a strong instrument for investors to analyze a company’s financial stability and performance. But it’s important to use ROE in conjunction with other financial metrics, while remaining mindful of industry-specific nuances. By holding the essence of ROE, you empower yourself to make well-informed decisions as you navigate the complex world of stock investments.
Frequently Asked Questions
The full form of “ROE” is “Return on Equity.
A high ROE typically indicates that a company is effectively using shareholder funds to generate profits. It suggests strong financial performance and efficient management
Yes, a company can have a negative ROE. This typically occurs when a company’s net income is negative or when its shareholders’ equity is significantly negative, often due to accumulated losses.
No, ROE is just one of many financial metrics to consider. Other metrics, such as earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, and debt-to-equity ratio, provide additional insights into a company’s financial performance and health.
Yes, ROE can be manipulated by a company through various means, such as using financial leverage (taking on debt) to increase equity returns. Investors should be cautious and consider the broader financial context when assessing ROE.